Installation
Helm or kubectl.Kyverno can be installed using Helm or deploying from the YAML manifests directly. When using either of these methods, there are no other steps required to get Kyverno up and running.
Kyverno must always be installed in a dedicated Namespace; it must not be co-located with other applications in existing Namespaces including system-level Namespaces such as kube-system.
Compatibility Matrix
Kyverno follows the same support policy as the Kubernetes project which is an N-2 policy in with the three latest minor releases are maintained. Although previous versions may work, they are not tested and therefore no guarantees are made as to their full compatibility. Kyverno also follows a similar strategy for support of Kubernetes itself. The below table shows the compatibility matrix.
| Kyverno Version | Kubernetes Min | Kubernetes Max |
|---|---|---|
| 1.6.x | 1.16 | 1.23 |
| 1.7.x | 1.21 | 1.23 |
| 1.8.x | 1.23 | 1.25 |
| 1.9.x | 1.24 | 1.26 |
* Due to a known issue with Kubernetes 1.23.0-1.23.2, support for 1.23 begins at 1.23.3.
Install Kyverno using Helm
Kyverno can be deployed via a Helm chart–the only supported method for a production install–which is accessible either through the Kyverno repo or on ArtifactHub.
In order to install Kyverno with Helm, first add the Kyverno Helm repository.
1helm repo add kyverno https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno/
Scan the new repository for charts.
1helm repo update
Optionally, show all available chart versions for Kyverno.
1helm search repo kyverno -l
Install Kyverno with three replicas for high-availability in a new Namespace:
1 helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno --create-namespace --set replicaCount=3
See High Availability and Standalone sections below for additional details.
To install the Kyverno Pod Security Standard policies run the below Helm command after Kyverno has been installed.
1helm install kyverno-policies kyverno/kyverno-policies -n kyverno
Notes for ArgoCD users
When deploying the Kyverno Helm chart with ArgoCD, you will need to enable Replace in the syncOptions. You probably want to also ignore diff in aggregated cluster roles (aggregated cluster roles are built by aggregating other cluster roles in the cluster and are dynamic by nature, therefore desired and observe states cannot match).
You can do so by following instructions in these pages of the ArgoCD documentation:
ArgoCD uses Helm only for templating but applies the results with kubectl. Unfortunately kubectl adds metadata that will cross the limit allowed by Kubernetes. Using Replace overcomes this limitation. Another option is to use server-side apply, supported in ArgoCD v2.5+.
Below is an example of an ArgoCD Application manifest that should work with the Kyverno Helm chart:
1apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
2kind: Application
3metadata:
4 name: kyverno
5 namespace: argocd
6spec:
7 destination:
8 namespace: kyverno
9 server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
10 project: default
11 source:
12 chart: kyverno
13 repoURL: https://kyverno.github.io/kyverno
14 targetRevision: 2.6.0
15 syncPolicy:
16 automated:
17 prune: true
18 selfHeal: true
19 syncOptions:
20 - CreateNamespace=true
21 - Replace=true
Ownership Clashes
ArgoCD automatically sets the app.kubernetes.io/instance label and uses it to determine which resources form the app. The Kyverno Helm chart also sets this label for the same purposes. In order to resolve this conflict, configure ArgoCD to use a different tracking mechanism as described in the ArgoCD documentation.
Notes for OpenShift Users
Red Hat OpenShift contains a feature called Security Context Constraints (SCC) which enforces certain security controls in a profile-driven manner. An OpenShift cluster contains several of these out of the box with OpenShift 4.11 preferring restricted-v2 by default. The Kyverno Helm chart defines its own values for the Pod’s securityContext object which, although it conforms to the upstream Pod Security Standards’ restricted profile, may potentially be incompatible with your defined Security Context Constraints. Deploying the Kyverno Helm chart as-is on an OpenShift environment may result in an error similar to “unable to validate against any security context constraint”. In order to get past this, deploy the Kyverno Helm chart with the --set securityContext=null flag. OpenShift will apply the defined SCC upon deployment. If on OpenShift 4.11+, the restricted-v2 profile is known to allow for successful deployment of the chart without modifying the Helm chart installation process.
High Availability
The official Helm chart is the recommended (and currently only supported) method of installing Kyverno in a production-grade, highly-available fashion as it provides all the necessary Kubernetes resources and configurations to meet production needs. By setting replicaCount=3, the following will be automatically created and configured as part of the defaults. This is not an exhaustive list and may change. For all of the default values, please see the Helm chart README keeping in mind the release branch. You should carefully inspect all available chart values and their defaults to determine what overrides, if any, are necessary to meet the particular needs of your production environment.
- Kyverno running with three replicas
- PodDisruptionBudget
- Pod anti-affinity configured
- Kyverno Namespace excluded
Note
Kyverno does not support two replicas. For a highly-available installation, the only supported count is three.By default, starting with the Helm chart version 2.5.0, the Kyverno Namespace will be excluded using a namespaceSelector configured with the immutable label kubernetes.io/metadata.name. Additional Namespaces may be excluded by configuring chart values. Both namespaceSelector and objectSelector may be used for exclusions.
See also the Namespace selectors section below and especially the Security vs Operability section.
Use Helm to create a Namespace and install Kyverno in a high availability configuration.
1helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno --create-namespace --set replicaCount=3
The Kyverno Pod Security Standard policies, an optional but recommended set of policies which implement the Kubernetes Pod Security Standards, must be added separately after Kyverno is installed.
1helm install kyverno-policies kyverno/kyverno-policies -n kyverno
Standalone
A “standalone” installation of Kyverno is suitable for lab, test/dev, or small environments where node count is less than three. It configures a single replica for the Kyverno Deployment and omits many of the production-grade components.
Use Helm to create a Namespace and install Kyverno.
1helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno --create-namespace --set replicaCount=1
To install pre-releases, add the --devel switch to Helm.
1helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno --create-namespace --devel
Install Kyverno using YAMLs
Kyverno can also be installed using a single installation manifest, however for production installation the Helm chart is the only supported method.
Pull from a release branch to install the stable releases including release candidates.
1kubectl create -f https://github.com/kyverno/kyverno/releases/download/v1.9.0/install.yaml
Security vs Operability
For a production installation, Kyverno should be installed in high availability mode. Regardless of the installation method used for Kyverno, it is important to understand the risks associated with any webhook and how it may impact cluster operations and security especially in production environments. Kyverno configures its resource webhooks by default (but configurable) in fail closed mode. This means if the API server cannot reach Kyverno in its attempt to send an AdmissionReview request for a resource that matches a policy, the request will fail. For example, a validation policy exists which checks that all Pods must run as non-root. A new Pod creation request is submitted to the API server and the API server cannot reach Kyverno. Because the policy cannot be evaluated, the request to create the Pod will fail. Care must therefore be taken to ensure that Kyverno is always available or else configured appropriately to exclude certain key Namespaces, specifically that of Kyverno’s, to ensure it can receive those API requests. There is a tradeoff between security by default and operability regardless of which option is chosen.
The following combination may result in cluster inoperability if the Kyverno Namespace is not excluded:
- At least one Kyverno rule matching on
Podsis configured in fail closed mode (the default setting). - No Namespace exclusions have been configured for at least the Kyverno Namespace, possibly other key system Namespaces (ex.,
kube-system). This is not the default as of Helm chart version 2.5.0. - All Kyverno Pods become unavailable due to a full cluster outage or improper scaling in of Nodes (for example, a cloud PaaS destroying too many Nodes in a node group as part of an auto-scaling operation without first cordoning and draining Pods).
If this combination of events occurs, the only way to recover is to manually delete the ValidatingWebhookConfigurations thereby allowing new Kyverno Pods to start up. Recovery steps are provided in the troubleshooting section.
Note
Kubernetes will not send ValidatingWebhookConfiguration or MutatingWebhookConfiguration objects to admission controllers, so therefore it is not possible to use a Kyverno policy to validate or mutate these objects.By contrast, these operability concerns can be mitigated by making some security concessions. Specifically, by excluding the Kyverno and other system Namespaces during installation, should the aforementioned failure scenarios occur Kyverno should be able to recover by itself with no manual intervention. This is the default behavior as of the Helm chart version 2.5.0. However, configuring these exclusions means that subsequent policies will not be able to act on resources destined for those Namespaces as the API server has been told not to send AdmissionReview requests for them. Providing controls for those Namespaces, therefore, lies in the hands of the cluster administrator to implement, for example, Kubernetes RBAC to restrict who and what can take place in those excluded Namespaces.
Note
Namespaces and/or objects within Namespaces may be excluded in a variety of ways including namespaceSelectors and objectSelectors. The Helm chart provides options for both, but by default the Kyverno Namespace will be excluded.Note
When using objectSelector, it may be possible for users to spoof the same label key/value used to configure the webhooks should they discover how it is configured, thereby allowing resources to circumvent policy detection. For this reason, a namespaceSelector using thekubernetes.io/metadata.name immutable label is recommended.The choices and their implications are therefore:
- Do not exclude system Namespaces, including Kyverno’s, (not default) during installation resulting in a more secure-by-default posture but potentially requiring manual recovery steps in some outage scenarios.
- Exclude system Namespaces during installation (default) resulting in easier cluster recovery but potentially requiring other methods to secure those Namespaces, for example with Kubernetes RBAC.
You should choose the best option based upon your risk aversion, needs, and operational practices.
Note
If you choose to not exclude Kyverno or system Namespaces/objects and intend to cover them with policies, you may need to modify the Kyverno resourceFilters entry in the ConfigMap to remove those items.Customize the installation of Kyverno
The picture below shows a typical Kyverno installation:
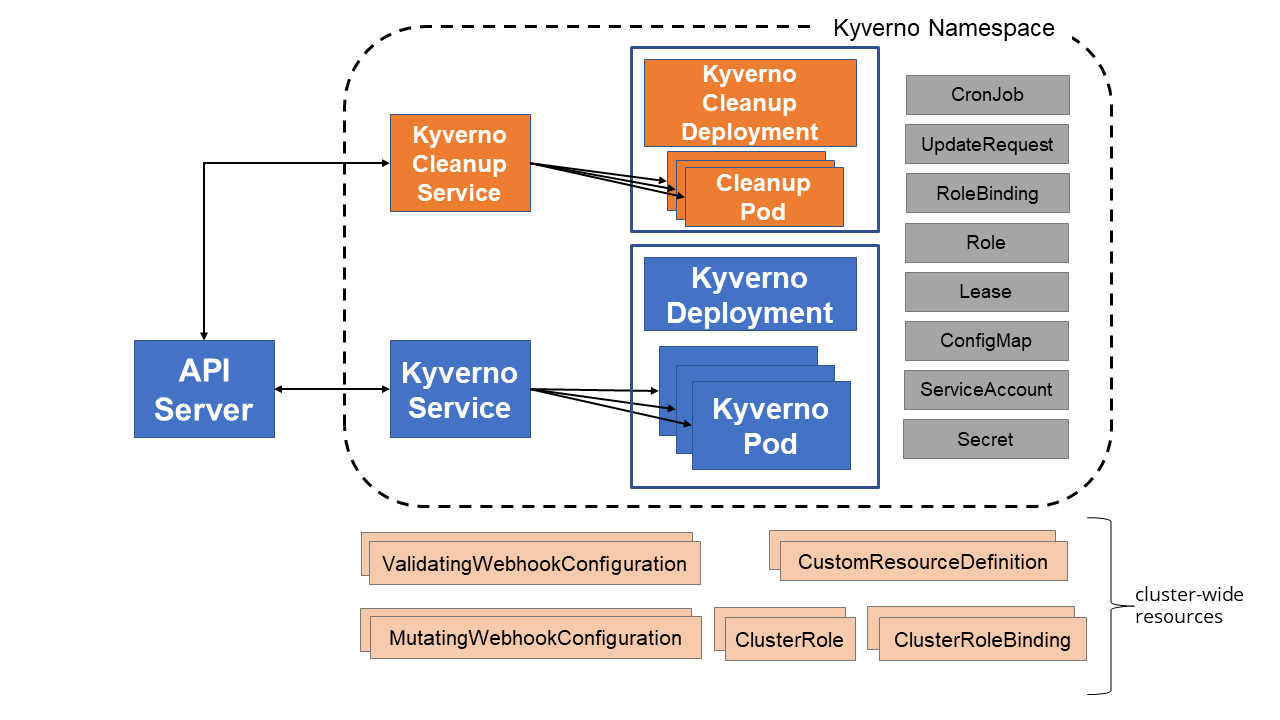
If you wish to customize the installation of Kyverno to have certificates signed by an internal or trusted CA, or to otherwise learn how the components work together, follow the below guide.
Installing a specific version
To install a specific version, locate the Helm chart version you wish to install and pass the chart version as the value of the --version flag.
1helm search repo kyverno -l | head -n 10
1helm install kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno --create-namespace --version 2.6.5
Alternatively, find the version of Kyverno you wish to install from the releases page and download and apply the install.yaml manifest directly.
Certificate Management
The Kyverno policy engine runs as an admission webhook and requires a CA-signed certificate and key to setup secure TLS communication with the kube-apiserver (the CA can be self-signed). There are two ways to configure secure communications between Kyverno and the kube-apiserver.
Option 1: Auto-generate a self-signed CA and certificate
Kyverno can automatically generate a new self-signed Certificate Authority (CA) and a CA signed certificate to use for webhook registration. This is the default behavior when installing Kyverno and expiration is set at one year. When Kyverno manage its own certificates, it will gracefully handle regeneration upon expiry.
Install Kyverno using one of the methods defined above.
To check the Kyverno controller status, run the command:
1## Check pod status
2kubectl get pods -n <namespace>
If the Kyverno controller is not running, you can check its status and logs for errors:
1kubectl describe pod <kyverno-pod-name> -n <namespace>
1kubectl logs -l app.kubernetes.io/name=kyverno -n <namespace>
Option 2: Use your own CA-signed certificate
You can install your own CA-signed certificate, or generate a self-signed CA and use it to sign a certificate. Once you have a CA and X.509 certificate-key pair, you can install these as Kubernetes Secrets in your cluster. If Kyverno finds these Secrets, it uses them. Otherwise it will create its own CA and sign a certificate from it (see Option 1 above). When you bring your own certificates, it is your responsibility to manage the regeneration/rotation process.
2.1. Generate a self-signed CA and signed certificate-key pair
Note
Using a separate self-signed root CA is difficult to manage and not recommended for production use.If you already have a CA and a signed certificate, you can directly proceed to Step 2.
Below is a process which shows how to create a self-signed root CA, and generate a signed certificate and key using step CLI:
- Create a self-signed CA
1step certificate create kyverno-ca rootCA.crt rootCA.key --profile root-ca --insecure --no-password
- Generate a leaf certificate with a five-year expiration
1step certificate create kyverno-svc tls.crt tls.key --profile leaf \
2 --ca rootCA.crt --ca-key rootCA.key \
3 --san kyverno-svc --san kyverno-svc.kyverno --san kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc --not-after 43200h --insecure --no-password
- Verify the contents of the certificate
1step certificate inspect tls.crt --short
The certificate must contain the SAN information in the X509v3 extensions section:
1X509v3 extensions:
2 X509v3 Subject Alternative Name:
3 DNS:kyverno-svc, DNS:kyverno-svc.kyverno, DNS:kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc
2.2. Configure Secrets for the CA and TLS certificate-key pair
You can now use the following files to create Secrets:
rootCA.crttls.crttls.key
To create the required Secrets, use the following commands (do not change the Secret names):
1kubectl create ns <namespace>
2kubectl create secret tls kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc.kyverno-tls-pair --cert=tls.crt --key=tls.key -n <namespace>
3kubectl create secret generic kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc.kyverno-tls-ca --from-file=rootCA.crt -n <namespace>
| Secret | Data | Content |
|---|---|---|
kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc.kyverno-tls-pair | tls.key & tls.crt | key and signed certificate |
kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc.kyverno-tls-ca | rootCA.crt | root CA used to sign the certificate |
Kyverno uses Secrets created above to setup TLS communication with the kube-apiserver and specify the CA bundle to be used to validate the webhook server’s certificate in the admission webhook configurations.
This process has been automated for you with a simple script that generates a self-signed CA, a TLS certificate-key pair, and the corresponding Kubernetes secrets: helper script
2.3. Install Kyverno
You can now install Kyverno by selecting one of the available methods from the installation section above.
Roles and Permissions
Kyverno creates several Roles, ClusterRoles, RoleBindings, and ClusterRoleBindings some of which may need to be customized depending on additional functionality required. To view all ClusterRoles and Roles associated with Kyverno, use the command kubectl get clusterroles,roles -A | grep kyverno.
Roles
Kyverno creates the following Roles in its Namespace:
kyverno:leaderelection: create, delete, get, patch, and update Leases to handle high availability configurations. get, list, patch, update, and watch Deployments so it can manage the Kyverno Deployment itself.kyverno-cleanup-controller: get, list, watch, create, and update Secrets. get, list, and watch ConfigMaps. create, delete, get, patch, and update Leases.
RoleBindings
Kyverno creates the following RoleBindings:
kyverno:leaderelection: manage leases for leader election across replicaskyverno-cleanup-controller: manages permissions bound to the ServiceAccount used by the cleanup controller
ClusterRoles
Kyverno uses aggregated ClusterRoles to search for and combine ClusterRoles which apply to Kyverno. The following ClusterRoles provide Kyverno with permissions to policies and other Kubernetes resources across all Namespaces:
kyverno: top-level ClusterRole which aggregates all other Kyverno ClusterRoleskyverno:policies: manages policies, reports, generate requests, report change requests, and statuskyverno:view: views all resourceskyverno:generate: creates, updates, and deletes resources via generate policy ruleskyverno:events: creates, updates, and deletes events for policy resultskyverno:userinfo: query Roles and RoleBinding configurations to build variables with Role information.kyverno:webhook: allows Kyverno to manage dynamic webhook configurationskyverno:cleanup-controller: allows the cleanup controller to manage webhooks, cleanup policies, and CronJobs it creates to perform the actual cleanup. This is the top-level ClusterRole which aggregates other ClusterRoles for use by the cleanup controller.kyverno:cleanup-controller:core: allows the cleanup controller to manage webhooks, cleanup policies, and CronJobs it creates to perform the actual cleanup. This ClusterRole is aggregated tokyverno-cleanup-controller.
Because aggregated ClusterRoles are used, there is only one ClusterRoleBinding named kyverno which binds the kyverno ClusterRole to the kyverno ServiceAccount.
Role aggregators
The following ClusterRoles are used to extend the default admin role with permissions to view and manage policy resources via role aggregation:
kyverno:admin-policies: allowadminrole to manage Policies and ClusterPolicieskyverno:admin-policyreport: allowadminrole to manage PolicyReports and ClusterPolicyReportskyverno:admin-reportchangerequest: allowadminrole to manage ClusterReportChangeRequests and ClusterReportChangeRequestskyverno:admin-updaterequest: allowadminrole to manage UpdateRequests
Customizing Permissions
Because the ClusterRoles used by Kyverno use the aggregation feature, extending the permission for Kyverno’s use in cases like mutate existing or generate rules is a simple matter of creating one or more new ClusterRoles which use the appropriate labels. It is no longer necessary to modify any existing ClusterRoles created as part of the Kyverno installation.
For example, if a new Kyverno policy introduced into the cluster requires that Kyverno be able to create or modify Deployments, this is not a permission Kyverno carries by default. It will be necessary to create a new ClusterRole and assign it the aggregation labels in order for those permissions to take effect.
Tip
To inspect the complete permissions granted to the Kyverno ServiceAccount via all the aggregated ClusterRoles, as well as the current labels used for aggregation, runkubectl get clusterrole kyverno -o yaml.This sample ClusterRole provides Kyverno additional permissions to create Deployments:
1apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2kind: ClusterRole
3metadata:
4 labels:
5 app.kubernetes.io/instance: kyverno
6 app.kubernetes.io/name: kyverno
7 app: kyverno
8 name: kyverno:create-deployments
9rules:
10- apiGroups:
11 - apps
12 resources:
13 - deployments
14 verbs:
15 - create
ConfigMap Flags
The following flags are used to control the behavior of Kyverno and must be set in the Kyverno ConfigMap.
excludeGroupRole: excludeGroupRole role expected string with comma-separated group role. It will exclude all the group role from the user request. Default we are usingsystem:serviceaccounts:kube-system,system:nodes,system:kube-scheduler.excludeUsername: excludeUsername expected string with comma-separated kubernetes username. In generate request if user enableSynchronizein generate policy then only kyverno can update/delete generated resource but admin can exclude specific username who have access of delete/update generated resource.generateSuccessEvents: specifies whether (true/false) to generate success events. Default is set to “false”.resourceFilters: Kubernetes resources in the format “[kind,namespace,name]” where the policy is not evaluated by the admission webhook. For example –filterKind “[Deployment, kyverno, kyverno]” –filterKind “[Deployment, kyverno, kyverno],[Events, *, *]”. Note that resource filters do not apply to background scanning mode.webhooks: specifies the Namespace or object exclusion to configure in the webhooks managed by Kyverno.
Container Flags
The following flags can also be used to control the advanced behavior of Kyverno and must be set on the main kyverno container in the form of arguments. Unless otherwise stated, all container flags should be prefaced with two dashes (ex., --autogenInternals).
admissionReports: enables the AdmissionReport resource which is created from validate rules inAuditmode. Used to factor into a final PolicyReport. Default istrue.allowInsecureRegistry: allows Kyverno to work with insecure registries (i.e., bypassing certificate checks) either with verifyImages rules or variables from image registries. Only for testing purposes. Not to be used in production situations.autoUpdateWebhooks: set this flag tofalseto disable auto-configuration of the webhook. With this feature disabled, Kyverno creates a default webhook configuration (which match all kinds of resources), therefore, webhooks configuration via the ConfigMap will be ignored. However, the user still can modify it by patching the webhook resource manually. Default istrue.backgroundScan: enables/disables background scans.trueby default.backgroundScanInterval: sets the time interval when periodic background scans take place. Default is1h. Supports minute durations as well (e.g.,10m).clientRateLimitBurst: configure the maximum burst for throttling. Uses the client default if zero. Default is50.clientRateLimitQPS: configure the maximum QPS to the control plane from Kyverno. Uses the client default if zero. Default is20.disableMetrics: specifies whether to enable exposing the metrics. Default isfalse.dumpPayload: toggles debug mode. When debug mode is enabled, the full AdmissionReview payload is logged. Additionally, resources of kind Secret are redacted. Default isfalse. Should only be used in policy development or troubleshooting scenarios, not left perpetually enabled.enableTracing: set to enable exposing traces. Default isfalse.enablePolicyException: set totrueto enable the PolicyException capability. Default isfalse.exceptionNamespace: set to the name of a Namespace where PolicyExceptions will only be permitted. PolicyExceptions created in any other Namespace will throw a warning. Implies theenablePolicyExceptionflag is set totrue.forceFailurePolicyIgnore: set to force Failure Policy toIgnore. Default isfalse.genWorkers: the number of workers for processing generate policies concurrently. Default is10.imagePullSecrets: specifies secret resource names for image registry access credentials. Only a single value accepted currently due to an upstream bug.imageSignatureRepository: specifies alternate repository for image signatures. Can be overridden per rule viaverifyImages.Repository.kubeconfig: specifies the Kubeconfig file to be used when overriding the API server to which Kyverno should communicate.leaderElectionRetryPeriod: controls the leader election renewal frequency. Default is2s.loggingFormat: determines the output format of logs. Logs can be outputted in JSON or text format by setting the flag tojsonortextrespectively. Default istext.maxQueuedEvents: defines the upper limit of events that are queued internally. Default is1000.metricsPort: specifies the port to expose prometheus metrics. Default is8000.otelCollector: sets the OpenTelemetry collector service address. Kyverno will try to connect to this on the metrics port. Default isopentelemetrycollector.kyverno.svc.cluster.local.otelConfig: sets the preference for Prometheus or OpenTelemetry. Set togrpcto enable OpenTelemetry. Default isprometheus.profile: setting this flag totruewill enable profiling. Default isfalse.profileAddress: Configures the address of the profiling server. Default is"".profilePort: specifies port to enable profiling. Default is6060.protectManagedResources: protects the Kyverno resources from being altered by anyone other than the Kyverno Service Account. Defaults tofalse. Set totrueto enable.reportsChunkSize: maximum number of results in generated reports before splitting occurs if there are more results to be stored. Default is1000.serverIP: Like thekubeconfigflag, used when running Kyverno outside of the cluster which it serves.transportCreds: set to the certificate authority secret containing the certificate used by the OpenTelemetry metrics client. Empty string means an insecure connection will be used. Default is"".-v: sets the verbosity level of Kyverno log output. Takes an integer from 1 to 6 with 6 being the most verbose. Level 4 shows variable substitution messages. Default is2.webhookRegistrationTimeout: specifies the length of time Kyverno will try to register webhooks with the API server. Defaults to120s.webhookTimeout: specifies the timeout for webhooks. After the timeout passes, the webhook call will be ignored or the API call will fail based on the failure policy. The timeout value must be between 1 and 30 seconds. Defaults is10s.
Policy Report access
During the Kyverno installation, it creates a ClusterRole kyverno:admin-policyreport which has permission to perform all operations on resources policyreport and clusterpolicyreport. To grant access to a Namespace admin, configure the following YAML file then apply to the cluster.
- Replace
metadata.namespacewith Namespace of the admin - Configure
subjectsfield to bind admin’s role to the ClusterRolepolicyviolation
1apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2kind: RoleBinding
3metadata:
4 name: policyviolation
5 # change namespace below to create rolebinding for the namespace admin
6 namespace: default
7roleRef:
8 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
9 kind: ClusterRole
10 name: kyverno:admin-policyreport
11subjects:
12# configure below to access policy violation for the namespace admin
13- kind: ServiceAccount
14 name: default
15 namespace: default
16# - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
17# kind: User
18# name:
19# - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
20# kind: Group
21# name:
Webhooks
The mutatingWebhookConfiguration and the validatingWebhookConfiguration resources are registered and managed dynamically based on the configured policies. With Kyverno-managed webhooks, Kyverno only receives admission requests for the matching resources defined in the policies, thereby preventing unnecessary admission requests being forwarded to Kyverno.
Additionally, the failurePolicy and webhookTimeoutSeconds policy configuration options allow granular control of webhook settings. By default, policies will be configured to “fail-closed” (i.e. the admission request will fail if the webhook invocation has an unexpected error or a timeout) unless the failurePolicy is set to Ignore.
This feature is enabled by default but can be turned off by the flag --autoUpdateWebhooks=false. If disabled, Kyverno creates the default webhook configurations that forwards admission requests for all resources and with FailurePolicy set to Ignore.
The spec.failurePolicy and spec.webhookTimeoutSeconds and policy configuration fields allow per-policy settings which are automatically aggregated and used to register the required set of webhook configurations.
Resource Filters
Resource filters are a way to instruct Kyverno which AdmissionReview requests sent by the API server to disregard. This is not the same ability as configuration of the webhook. The Kubernetes kinds that should be ignored by policies can be filtered out by modifying the value of data.resourceFilters in the kyverno ConfigMap stored in Kyverno’s Namespace. The default name of this ConfigMap is kyverno but can be changed by modifying the value of the environment variable INIT_CONFIG in the Kyverno deployment spec. data.resourceFilters must be a sequence of one or more [<Kind>,<Namespace>,<Name>] entries with * as a wildcard. Thus, an item [Secret,*,*] means that admissions of kind Secret in any Namespace and with any name will be ignored. Wildcards are also supported in each of these sequences. For example, this sequence filters out kind Pod in Namespace foo-system having names beginning with redis.
[Pod,foo-system,redis*]
By default a number of kinds are skipped in the default configuration including Nodes, Events, APIService, SubjectAccessReview, and more.
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: ConfigMap
3metadata:
4 name: kyverno
5 namespace: kyverno
6data:
7 # resource types to be skipped by Kyverno
8 resourceFilters: '[*,kyverno,*][Event,*,*][*,kube-system,*][*,kube-public,*][*,kube-node-lease,*][APIService,*,*][TokenReview,*,*][SubjectAccessReview,*,*][SelfSubjectAccessReview,*,*][Binding,*,*][ReplicaSet,*,*][AdmissionReport,*,*][ClusterAdmissionReport,*,*][BackgroundScanReport,*,*][ClusterBackgroundScanReport,*,*][ClusterRole,*,kyverno:*][ClusterRoleBinding,*,kyverno:*][ServiceAccount,kyverno,kyverno][ConfigMap,kyverno,kyverno][ConfigMap,kyverno,kyverno-metrics][Deployment,kyverno,kyverno][Job,kyverno,kyverno-hook-pre-delete][NetworkPolicy,kyverno,kyverno][PodDisruptionBudget,kyverno,kyverno][Role,kyverno,kyverno:*][RoleBinding,kyverno,kyverno:*][Secret,kyverno,kyverno-svc.kyverno.svc.*][Service,kyverno,kyverno-svc][Service,kyverno,kyverno-svc-metrics][ServiceMonitor,kyverno,kyverno-svc-service-monitor][Pod,kyverno,kyverno-test]'
To modify the ConfigMap, use existing tools and processes to edit the contents. Changes to the ConfigMap will automatically be picked up at runtime. Resource filters may also be configured at installation time via a Helm value.
Namespace Selectors
Instead of (or in addition to) directly ignoring the resources Kyverno processes, it is possible to instruct the API server to not send AdmissionReview requests at all for certain Namespaces based on labels. Kyverno can filter on these Namespaces using a namespaceSelector object by adding a new webhooks object to the ConfigMap. For example, in the below snippet, the webhooks object has been added with a namespaceSelector object which will filter on Namespaces with the label kubernetes.io/metadata.name=kyverno. The effect this will produce is the Kubernetes API server will only send AdmissionReview requests for resources in Namespaces except those labeled with kubernetes.io/metadata.name equals kyverno. The webhooks key only accepts as its value a JSON-formatted namespaceSelector object. Note that when installing Kyverno via the Helm chart and setting Namespace exclusions, it will cause the webhooks object to be automatically created in the Kyverno ConfigMap. The Kyverno Namespace is excluded by default.
1apiVersion: v1
2data:
3 resourceFilters: '[Event,*,*][*,kube-system,*][*,kube-public,*][*,kube-node-lease,*][Node,*,*][APIService,*,*][TokenReview,*,*][SubjectAccessReview,*,*][SelfSubjectAccessReview,*,*][*,kyverno,*][Binding,*,*][ReplicaSet,*,*][ReportChangeRequest,*,*][ClusterReportChangeRequest,*,*]'
4 webhooks: '[{"namespaceSelector":{"matchExpressions":[{"key":"kubernetes.io/metadata.name","operator":"NotIn","values":["kyverno"]}]}}]'
5kind: ConfigMap
6metadata:
7 name: kyverno
8 namespace: kyverno
Resource Requests and Limits
Because Kyverno is an admission controller with many capabilities and due to the variability with respect to environment type, size, and composition of Kubernetes clusters, the amount of processing performed by Kyverno can vary greatly. Sizing a Kyverno installation based solely upon Node or Pod count is often not appropriate to accurately predict the amount of resources it will require. For example, a large production cluster hosting 60,000 Pods yet with no Kyverno policies installed which match on Pod has no bearing on the resources required by Kyverno. Because webhooks are dynamically managed by Kyverno according to the policies installed in the cluster, no policies which match on Pod results in no information about Pods being sent by the API server to Kyverno and, therefore, reduced processing load.
The following is a table of test results observed on a highly available Kyverno 1.8.2 installation with a 4 Gi memory limit, all the Pod Security Standards policies installed (restricted profile) in which four were in Audit mode, and background scanning enabled. ARPS is admission requests per second and QPS is client queries per second. Tests were performed with the ClusterLoader2 tool. CPU and memory figures represent peak consumption. CPU represents physical cores of utilization total across all replicas with a frequency max of 3.35 GHz. Memory is per replica.
| Test | Policies | Nodes | Pods | ARPS | QPS | Memory | CPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 | 40 | 1192 | 10 | 41 | 400 Mi | 6 |
| 2 | 17 | 50 | 1444 | 11 | 30 | 364 Mi | 7 |
We recommend conducting tests in your own environment to determine real-world utilization in order to best set resource requests and limits, but as a best practice we also recommend not setting CPU limits.
Proxy
Kyverno supports using of a proxy by setting the standard environment variables, HTTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY, and NO_PROXY. These variables must be defined for the main Kyverno container in the Kyverno Deployment resource.
Upgrading Kyverno
Upgrading Kyverno is as simple as applying the new YAML manifest, or using Helm depending on how it was installed. You cannot upgrade Kyverno by bumping the image tag on the Deployment as this will not affect the CRDs and other resources necessary for Kyverno’s operation.
Upgrade Kyverno with YAML manifest
Apply the new manifest over the existing installation.
1kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kyverno/kyverno/releases/download/v1.9.0/install.yaml
Upgrade Kyverno with Helm
Kyverno can be upgraded like any other Helm chart.
Scan your Helm repositories for updated charts.
1helm repo update
Show the versions of the Kyverno chart which are available. To see pre-release charts, add the --devel flag to the helm command.
1helm search repo kyverno
Run the upgrade command picking the target version.
1helm upgrade kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno --version <version_number>
Uninstalling Kyverno
To uninstall Kyverno, use either the raw YAML manifest or Helm. The Kyverno deployment, RBAC resources, and all CRDs will be removed, including any reports.
Option 1 - Uninstall Kyverno with YAML manifest
1kubectl delete -f https://github.com/kyverno/kyverno/releases/download/v1.9.0/install.yaml
Option 2 - Uninstall Kyverno with Helm
1helm uninstall kyverno kyverno/kyverno -n kyverno
Clean up Webhook Configurations
Kyverno by default will try to clean up all its webhook configurations when terminated. But in cases where its RBAC resources are removed first, it will lose the permission to do so properly.
If manual webhook removal is necessary, use the below commands.
1kubectl delete mutatingwebhookconfigurations kyverno-policy-mutating-webhook-cfg kyverno-resource-mutating-webhook-cfg kyverno-verify-mutating-webhook-cfg
2
3kubectl delete validatingwebhookconfigurations kyverno-policy-validating-webhook-cfg kyverno-resource-validating-webhook-cfg kyverno-cleanup-validating-webhook-cfg